ABOUT THIS CONTENT
Strategic Group Analysis looks at players’ positions in the competitive environment and the underlying factors that determine a company’s profitability, as well as the competitive dynamics of an industry.Subject: Strategy/Frameworks
Table of Contents
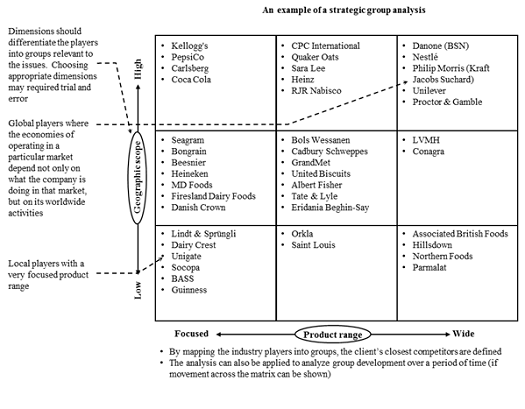
Strategic Group Analysis looks at players’ positions in the competitive environment and the underlying factors that determine a company’s profitability, as well as the competitive dynamics of an industry. It attempts to characterize the strategies of all significant competitors along broad strategic dimensions. These dimensions differentiating players into strategic groups must be chosen with respect to industry structure, profitability factors, and the project issues being addressed.
Strategic groups can be created based on many dimensions:
- Specialization
- Brand identification
- Push vs pull
- Channel selection
- Product quality
- Technological position
- Vertical integration
- Cost position
- Service
- Price policy
- Financial or operating leverage
- Parent company relationship
- Government relationship
It can often be useful to generically differentiate the groups based on “How they compete” and “Where they compete.”
Methodology
- Collect outcomes of the Players Analysis.
- Determine dimensions. Identify the players and choose the most relevant dimensions that differentiate the players into groups corresponding to the issues being addressed.
- Group players. Position the client and competitors in the matrix.
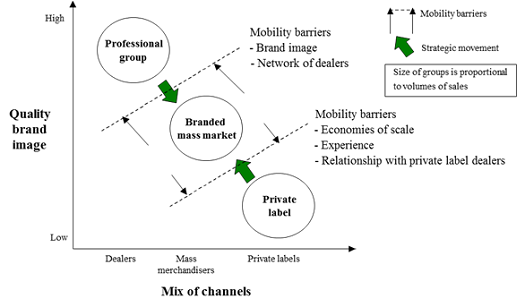
- Evaluate group mobility and direction. Evaluate the strategic intent of individual companies as well as industry trends and barriers to entry/exit to determine potential movements within and between groups.
Notes
- A strategic group is the group of firms in an industry following the same or similar strategy along strategic dimensions
- Strategic groups are characterized by barriers to entry and exit and by “mobility barriers,” that make it more difficult for firms to move between groups. Such mobility barriers are due to market structure, technology, strategy or customer characteristics
- Profitability at a corporate view may be the driver for strategic groups while at a business unit level other dimensions might be more important determinants of strategic groups
- Dimensions whereby strategic groups are identified must be carefully selected to be of relevance
- Strategic group dimensions should be chosen on the basis of the identified issues
- There are not simply two generic dimensions that can categorize all industries; rather, there are many
Strengths
- Assesses strategic dynamics and shifts in the industry
- Defines the nearest competitors of the company and assists in evaluating the differences in strategies of these competitors
- Helps assess current and potential strategic movements of the competitors in the market
- Helps understand the underlying determinants of a firm’s profitability
Weaknesses
- Heavily relies on a thorough understanding of the market and its players to identify mobility barriers and barriers to entry/exit
- Competitor goals and strategies are often unclear
- May require trial and error to find useful dimensions
- “Wrong” dimensions will not differentiate groups into useful categories
There Are No Comments
Click to Add the First »
Click to Add the First »
